If you’re considering opening a bank account or exploring payment options, it’s important to understand these differences, especially with products like CIMB’s CASA or Alliance SavePlus Account-i, which offer unique benefits tied to debit card usage.
1. How They Work
- Credit Card: When you use a credit card, you are borrowing money from the bank or credit card issuer to make purchases. You can spend up to a certain credit limit set by the bank based on your income and creditworthiness. You’ll need to repay the borrowed amount, typically on a monthly billing cycle, and if you carry a balance, you’ll incur interest charges.
- Debit Card: A debit card is linked directly to your bank account. When you make a purchase, the money is immediately withdrawn from your account, meaning you can only spend the funds you already have. You won’t accumulate debt, but if your account balance is low, your spending is limited.
2. Spending Limit
- Credit Card: Your credit limit determines how much you can spend using your credit card. Credit limits can be substantial for Malaysians with higher incomes and good credit scores. However, overspending beyond your means can lead to debt and interest charges if you don’t pay off your balance in full each month.
- Debit Card: Your spending limit with a debit card is the available balance in your bank account. You cannot spend more than what you have, so there’s no risk of accumulating debt, but it’s crucial to keep an eye on your account balance to avoid overdraft fees.
3. Interest Charges and Fees
- Credit Card: If you do not pay off your credit card balance by the due date, you’ll incur interest charges. Credit card interest rates in Malaysia can range from 15% to 18% per annum. There may also be annual fees, late payment charges, and cash advance fees for certain card services.
- Debit Card: Debit cards have no interest charges because you’re using your own money. Debit cards generally have fewer fees, though you may be charged for certain transactions, such as using another bank’s ATM or if you make international purchases.
4. Credit Score Impact
- Credit Card: Credit cards are tied to your credit score. If you use your credit card responsibly—making timely payments and keeping your balance low—you can improve your credit score. A good credit score can help you secure loans, better interest rates, or higher credit limits in the future. However, missing payments or maxing out your card can damage your credit score.
- Debit Card: Debit card transactions are not reported to credit bureaus, so they do not impact your credit score. While this means there’s no risk of negatively affecting your score, it also means you’re not building a credit history by using your debit card.
5. Rewards and Perks
- Credit Card: One of the biggest advantages of credit cards is their rewards. Depending on the card, you can earn cashback, points, or air miles for your spending. Many Malaysian credit cards also offer perks like discounts, free travel insurance, and access to airport lounges. These rewards can be valuable if you use your card frequently and pay off the balance each month.
- Debit Card: While some Malaysian debit cards offer basic rewards or cashback programs, they tend to be less generous than credit card rewards. Debit card perks are generally limited, and you won’t find the same level of benefits, such as free travel insurance or exclusive discounts.
6. Protection and Fraud
- Credit Card: Credit cards offer greater protection against fraud. If your card is stolen or unauthorized transactions occur, you can dispute the charges with your bank. In most cases, you won’t be held liable for fraudulent charges, and the bank will investigate the issue. Credit cards also often offer purchase protection and extended warranties on items you buy.
- Debit Card: While debit cards offer protection against fraud, it can be riskier if your card is stolen. Since the money is directly withdrawn from your account, you may have to wait for an investigation before getting your money back. Some banks offer purchase protection on debit card transactions, but the coverage is typically less extensive than credit cards.
7. Best Use Cases
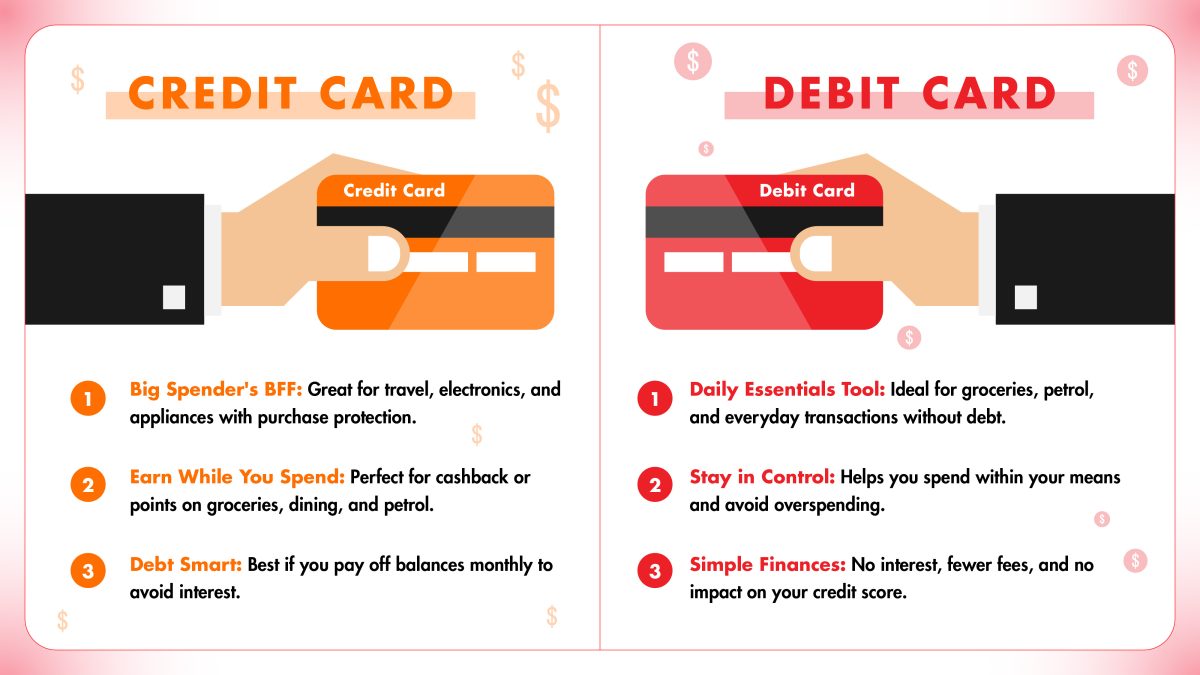
Are You Ready for a Credit Card?
Debit cards are a necessity for anyone with a bank account, making them an integral part of everyday financial life. With the rise of digital banking, even digital debit cards are becoming the norm. On the other hand, credit cards are optional and require careful consideration.
If you’re ready to commit to building credit, earning rewards, and enjoying added protections, a credit card may suit your needs. However, for those who prefer spending only what they have, avoiding debt, and simplifying financial management, CIMB CASA or Alliance SavePlus Account-i provide excellent debit card solutions.
Whether you’re looking to open a basic savings account with CIMB CASA or explore the flexible, Shariah-compliant features of the Alliance SavePlus Account-i, both options come with essential debit card benefits tailored to your financial needs. Choose the account that fits your lifestyle and take control of your spending today.

